
Innovation


Cow Enzyme Fights Superbugs: A Breakthrough in Antibiotic ResistanceJuly 9, 2025

New Study: The Secret Within Tumors That Could Explain Racial Disparities in CancerJune 15, 2025
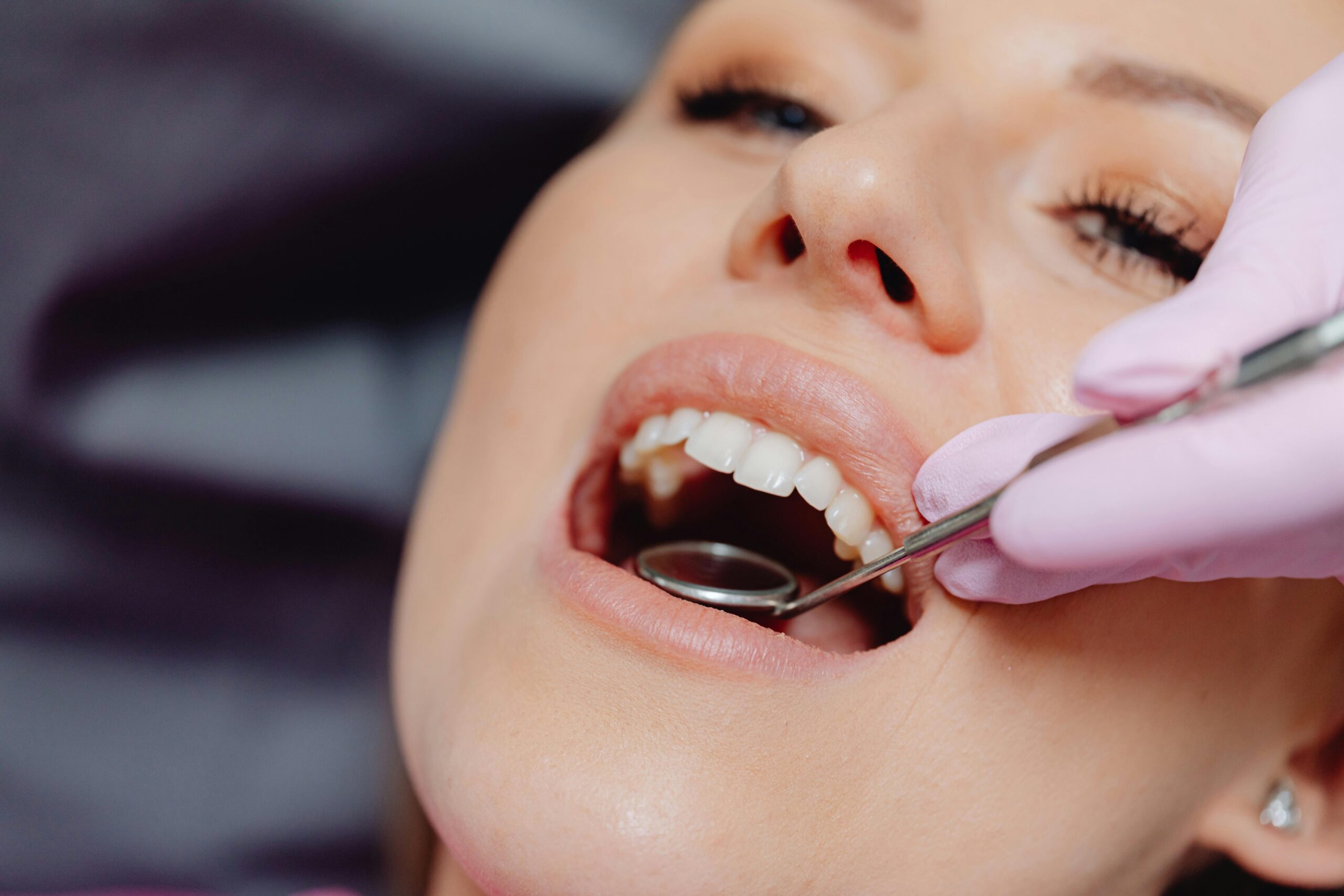
The Hidden Connection: How Oral Bacteria Signal Colorectal Cancer RiskJune 8, 2025

Game Changer: Oral Pill Shows Promise for Battling Future PandemicsMay 31, 2025

Your City’s Rats Are Becoming More Alike, Down to Their Guts. Here’s WhyMay 25, 2025
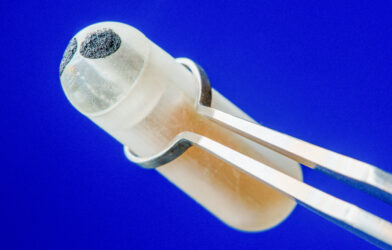
This Innovative ‘Smart Pill’ Could Take Gut Health Research, Treatments To New HeightsAugust 8, 2023

Skin sensors provide non-invasive, cost-effective means for diagnosing gut conditionsOctober 12, 2022
Stanford researchers design fully functional synthetic microbiome, opening new doors into gut-disease linksOctober 10, 2022
