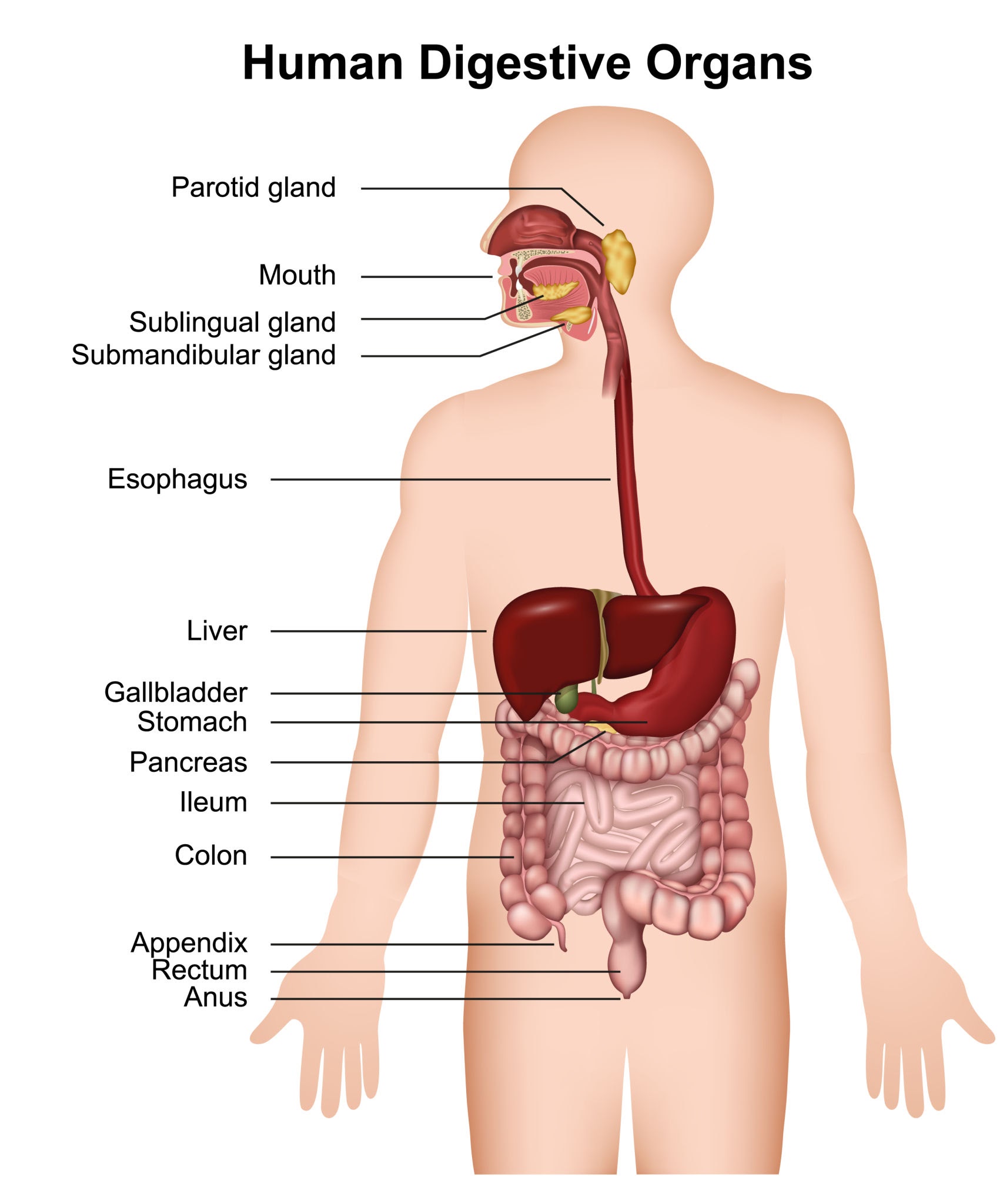
Gut Health

The Gut Revolution: How One Probiotic Strain Could Change Everything for Inflammatory DiseaseAugust 23, 2025
Your Mouth Bacteria Could Be Driving Oral Cancer SpreadAugust 22, 2025

Could gut bacteria be the new frontier for space medicine?August 20, 2025

What you eat could be shaping your personal microbiomeAugust 20, 2025

Study Finds Gut Bacteria Can Predict Success of Mesothelioma TherapyAugust 19, 2025
The Countdown to Mars Starts in Your Gut, According to New StudyAugust 17, 2025

From Digestion to Disease: The Surprising Power of Your Gut MicrobiomeAugust 16, 2025

The Secret Life Inside a Dolphin’s Gut, ExposedAugust 14, 2025