Microbiome


New biotherapeutic protects gut microbiome from harmful effects of antibioticsJune 6, 2022

Scientists figure out why gut bacteria make some blood pressure medications less effectiveJune 2, 2022

Even microscopic animals have diverse microbiomes, scientists showJune 1, 2022
Here’s how microbes key to digestion also keep gut function in checkMay 20, 2022
Fungus in the gut: One type is more friend than foe — when it ‘introduces’ itself firstMay 18, 2022
Link between statins and gut microbiome could lead to personalized treatments for high cholesterolMay 17, 2022
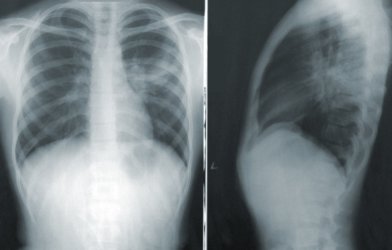
Pneumonia severity, risk of death hinges on gut bacteria for older adultsMay 16, 2022

Frequent UTIs could be caused by antibiotics and gut bacteria, study showsMay 11, 2022